Basic digitization settings
No matter what you do, 2 business goals are common to all – to improve the user experience and increase efficiency.
When it comes to working with documents, two strategic determinants are key to achieving these goals:
If they are in physical form, we convert them into electronic form immediately upon entering the organization.
We create, process, save and keep all documents in electronic form.
In order for these strategies to become a practice, it is often necessary to optimize certain business processes. Application digitization of documentation ensures work with documents with minimal time and energy, simplifying work with digital documents compared to working with paper ones.
Universal access to documents regardless of the form and location of storage
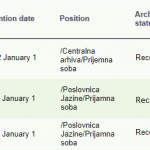
Every received or created document needs to be saved in such a way that we can get it as easily as possible in case of need. However, although we have all of them in digital form, some of them still need to be preserved in their (original) physical form according to the law.
By digitizing original paper documents and adequately marking (indexing) digitized documents, the requirement to quickly find digitized documents is reduced to the characteristics and speed of computers, computer databases and other technology used in the process and quality, accurate and correct marking.
In order to make the management of a large amount of archived documentation as simple as possible and not to bother with the way it was received, it is necessary to provide a system within which you have information from each interface at any time where each archived document is located. Also, in the case of using multiple different repositories in the organization (Alfresco, SharePoint, FileNet, OpenText, etc.), based on different technologies, simultaneous operation and use of the system is ensured.
Optimization of physical archive management
The hybrid approach to record management and the location tracking system of each document also allows you to optimize the management of the physical archive, by providing you with:
- accessing functionalities through a solution interface or existing applications,
- physical positioning in several locations (temporarily in branches or permanently in a warehouse),
- connection (integration) with specialized, CAS (Content-Addressable Storage) storage systems,
- full management of archived material (creation, search, reverses, extraction, relocation and destruction).
- full supervision of the work of the archive with access rights and detailed reports.
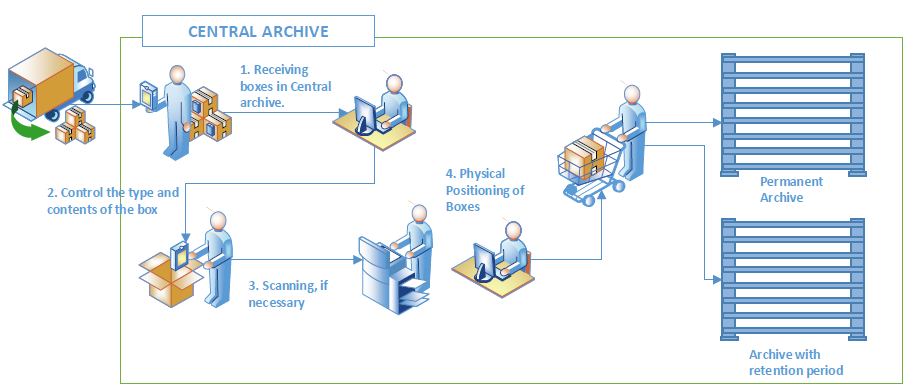
Managing a physical archive in 7 steps
Preparation of shipment
The process consists of creating a box, packing the documentation into boxes and after closing them, packing the boxes into shipments. Each segment is marked with its own barcode, which provides support for controlling the transport of documents between locations (from the branch to the central location).
After receiving the shipment (shipment in boxes), the complete documentation is controlled, if necessary scanned, archived and positioned for:
- storage (permanently or temporarily for a certain period),
- destruction and destruction records,
- issuance of reverse.
Receipt of shipment
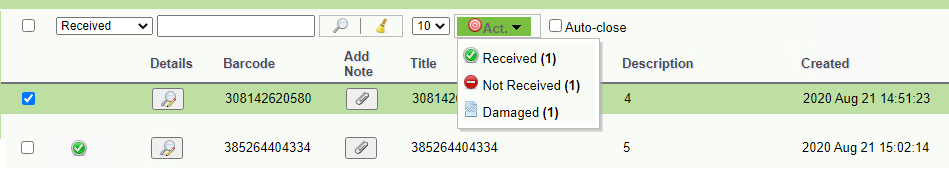
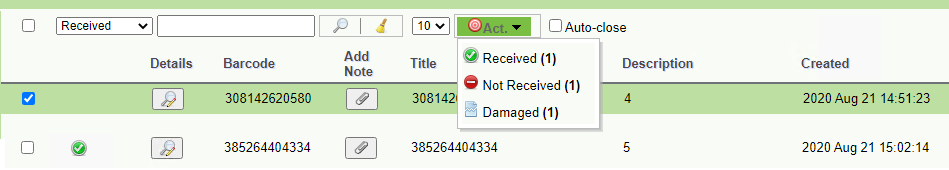
When you receive a shipment and view the contents of the box, you must receive it within the application by selecting one of the following actions from the drop-down menu:
• Received in the Archive,
• Not received in the Archive,
• Received in the Archive (damaged).
Information about the shipment – whether the boxes were received, whether there was damage in transport, whether any document is missing, etc., are also visible to the owners of the documentation (employees of the branch) who created the boxes and sent them to the Archive.
After closing the shipment view, you can begin the scan and the process of positioning the box on the shelf within the Permanent or Temporary Archive.
Documentation scanning
Within the scanning functionality for each type of documentation, there is a predefined business process according to your specific needs.
After scanning the contents of the archive box, you physically return the documents to the corresponding box and start the physical and application positioning on the shelves.
Archiving and positioning of documentation
After saving or application positioning of the box, its storage position is automatically visible within the application. The system also allows you to manually change the location of the box by selecting an existing vacant position in the archive, which frees the previously reserved (filled) position.
From the moment of application creation of the box until the moment of its destruction, the user is enabled to create a box report that changes dynamically depending on changes in metadata of box contents (added new documentation type, deleted documentation, change of content description, change of box location…). So even after positioning the box on the shelf, in addition to a digital record of the contents and location, there is also a visual display of the contents of the box that is physically glued to the box in the form of a report.
Withdrawal and return of documentation to the Archive
Withdrawal from the physical archive is performed when the user's request for the issuance of the box (or the documentation contained in it) arrives for inspection or re-operation.
The request for issuing a box for inspection is possible only on archived (positioned) boxes in the Archive.
For all issued boxes, the initial position is kept in the archive so that upon return, each can be placed in the same position from which it was issued.
Destruction of documentation
The system automatically reports when the box retention period has expired so that the documentation inside it can be destroyed.
After the application destroys the box, the status changes to ˝Destroyed˝ and the position for new boxes is freed. Along with the status, the date and name of the user who performed the destruction are visible.
Document Record Retention and Disposition Policy
The system allows you to store documents or objects for a certain number of years in one storage location, and after that period they are transferred to another segment of the archive. Also, in case the subject becomes part of the court process, it is transferred to a special part of the archive - LegalHold.